I have just purchased an ONU/ONT Fiberhome AN5506-01-A at AliExpress a well known online store in Asia region. I decided to buy it because of my Fiber Internet Service Provider is locking down all their Optical Network Unit aka Optical Network Terminal which only allow their subscriber to a limited privileges to the CPE device settings and configurations. My ISP are updating their device remotely via OMCI and not through TR069, the updates or the ONU firmware upgrade is done without your knowing to whether it is online or offline it can be done. Exactly the updates upon updates is done prior without noticed the so called firmware!
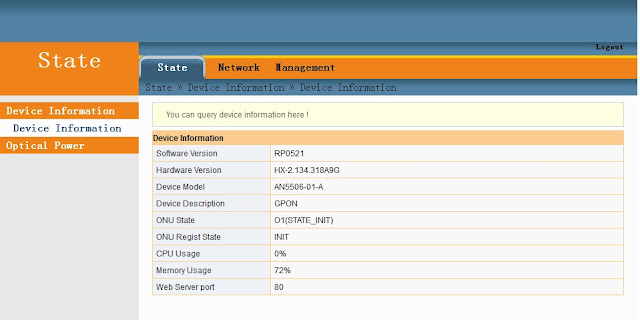
My problem is that the ONU AN5506-01-A came in to me is with the Software Version RP0521 and the Hardware Version is HX-2.134.318A9G, this stock firmware also has a limited basic configuration settings. Meaning some of the Menus and sub-menus are being omitted, you can not set the WAN to Bridge Mode on the web Graphical User Interface (GUI) its explicitly as Router mode only. Another thing is that the LAN menu or the setting is missing from the GUI, you can not modify your desired IP configuration, enabling and disabling DHCP server and relay are out of the context. Most of all its NOT a plug and play electronics equipment.
Why do I need to change the MAC Addresses?
Unlike xDSL internet connection, your ISP will just ask you what username and password you wish or they just provide you the username and the password for you such as yourname@isp and your password, most often you can even choose your desired password as you wish for it. Then choosing and buying your own personal wireless modem router from low to mid or high class residential gateway is just on your finger nail because the device is a plug and play after you input the given username and password given by your ISP its now connected to the internet.
Now here we go, I took the fiber patch cord from my ONU/ONT ISP and then plug it to my new Fiberhome AN5506-01-A the LOS LED turns off from blinking Red, and the PON LED now don't stop from blinking Yellow. Obviously the PON LED means that the ONU is not connected to the network or to the OLT it needs an authentication, once the ONU is connected the PON LED lit will be steady in yellow color.
To get the AN5506-01-A to be connected to the OLT of my ISP we need to copy first the PON MAC address of the ONU/ONT and Serial Number of it that was provided by the ISP and replicate to the new ONU/ONT AN5506-01-A.
How do we change the PON MAC Address of the Fiberhome AN5506-01-A?
The ONU/ONT Fiberhome An5506-01-A is a ARM Linux Embeded system, going to the web GUI there is no way of changing the PON MAC Address. The chances of spoofing the Passive Optical Network MAC address is in the Linux environment, we can log in via Telnet and we can get access to its Command Line Interface (CLI), after reviewing the commands it is very reluctant to clone the MAC address. Another option is thru Serial communication port, this is a terminal also a CLI were we can get help from Busybox.
To change the PON MAC Address of AN5506-01-A heres the command.
First find the physical MAC address of your ONU/ONT device by running this following command :
# ifconfig -a | grep HWaddr
pie0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E
The hexadecimal numbers in
blue denote my AN5506-01-A ONU/ONT PON MAC address.
Next, type this following commands.
# ifconfig pie0 down
# ifconfig pie0 hw ether 00:A1:B2:C3:D4:E5
# ifconfig pie0 up
# ifconfig pie0 |grep HWaddr
To check again if the PON MAC Address have been change already just repeat this following command.
# ifconfig -a | grep HWaddr
pie0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:A1:B2:C3:D4:E5
This is just a temporary solution, once the machine is being rebooting it will just go back to its original MAC address.
The final option we can do is still via Serial port but now it would be thru U-Boot Linux environment. Power ON the ONU/ONT
then you will see U-Boot started you must be quick in 3 seconds it will continue to boot to the second level of booting. You have to hit any key in 3 seconds.
U-Boot 2010.03-svn462977 (Mar 09 2016 - 17:03:30)
DRAM: 16 MB
Boot From SPI Flash
CHIP ID = 51161110
NAND: SFC ID: 0x0
SFC : cs0 unrecognized JEDEC id 00000000, extended id 00000000
SFC ID: 0xef4018
SFC: cs1 W25Q128BV (16384 Kbytes)
SFC: Detected W25Q128BV with page size 65536, total 16777216 bytes
SFC: sfc_read flash offset 0x40000, len 0x20000, memory buf 0x81560008
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 2
Here's the following command in U-boot.
# setenv ponmac 00:A1:B2:C3:D4:E5
# saveenv
saveenv command means saving the environment variables. This will save permanently to the SPI FLASH storage.
Saving Environment to SPI Flash...
Erasing SPI flash...SFC: erase offset 0x40000, len 0x20000
erase cs 1
Writing to SPI flash...SFC: sfc_write flash to 0x40000, len 0x20000, memory buf 0x81560008
Erasing SPI flash...SFC: erase offset 0x60000, len 0x20000
erase cs 1
Writing to SPI flash...SFC: sfc_write flash to 0x60000, len 0x20000, memory buf 0x81560008
done
You must see something like this log messages.
Finally you can now use your ONU/ONT AN5506-01-A, just input the Serial Number of your device the OLT of your ISP provider will now give the authority to be connected to the system.